🔌 1. Modem (Modulator-Demodulator)
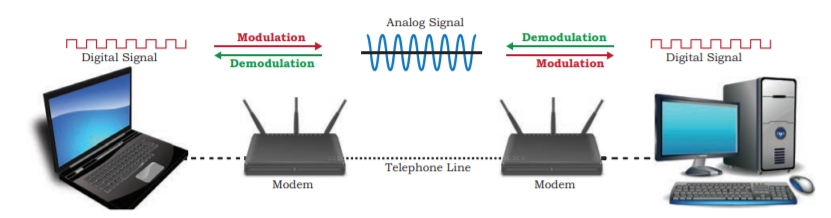
Converts digital signals from a computer into analog signals for transmission over telephone lines and vice versa.
Used to connect to the Internet over telephone lines (DSL).
When you use a telephone wire to connect to the Internet, your ISP provides a modem to connect your home network.
📶 2. Router

- Forwards data packets between different networks (like your home network and the Internet)
- Assigns local IP addresses and provides Network Address Translation (NAT)
- Connects multiple networks
- Directs traffic based on IP addresses
- Often includes firewall, DHCP, and wireless access point features
Used in homes and businesses to connect to the internet and route data to the correct devices.
Routing algorithms in networking are methods used to determine the best path for data to travel from a source to a destination across a network. Think of it like GPS for your data packets—choosing which roads (network links) to take to reach the destination efficiently.
1. Purpose of Routing Algorithms:
- Find optimal paths (shortest or fastest route).
- Avoid network congestion.
- Ensure reliability and fault tolerance.
- Support dynamic changes in network topology.
2. Types of Routing Algorithms:
- Static Routing:
- Routes are manually configured by network administrators.
- Do not change automatically if network topology changes.
- Simple but not adaptable to failures.
- Example: Routing table in a small office network.
- Dynamic Routing:
- Routes are automatically updated using algorithms.
- Responds to network failures or congestion.
- Divided into:
- Distance Vector Routing: Each router shares its routing table with neighbors. Uses metrics like hop count. Examples: RIP, IGRP. Pros: Simple; Cons: Slow convergence.
- Link State Routing: Each router maintains a full network map and computes shortest paths using algorithms like Dijkstra. Examples: OSPF, IS-IS. Pros: Fast and accurate; Cons: Requires more memory and CPU.
- Hybrid Routing: Combines features of distance vector and link state. Example: EIGRP.
3. Metrics Used in Routing:
- Hop count: Number of routers to the destination.
- Bandwidth: Link capacity.
- Delay: Time taken for data to travel.
- Cost: Abstract value combining multiple factors.
- Reliability: Likelihood of link failure.
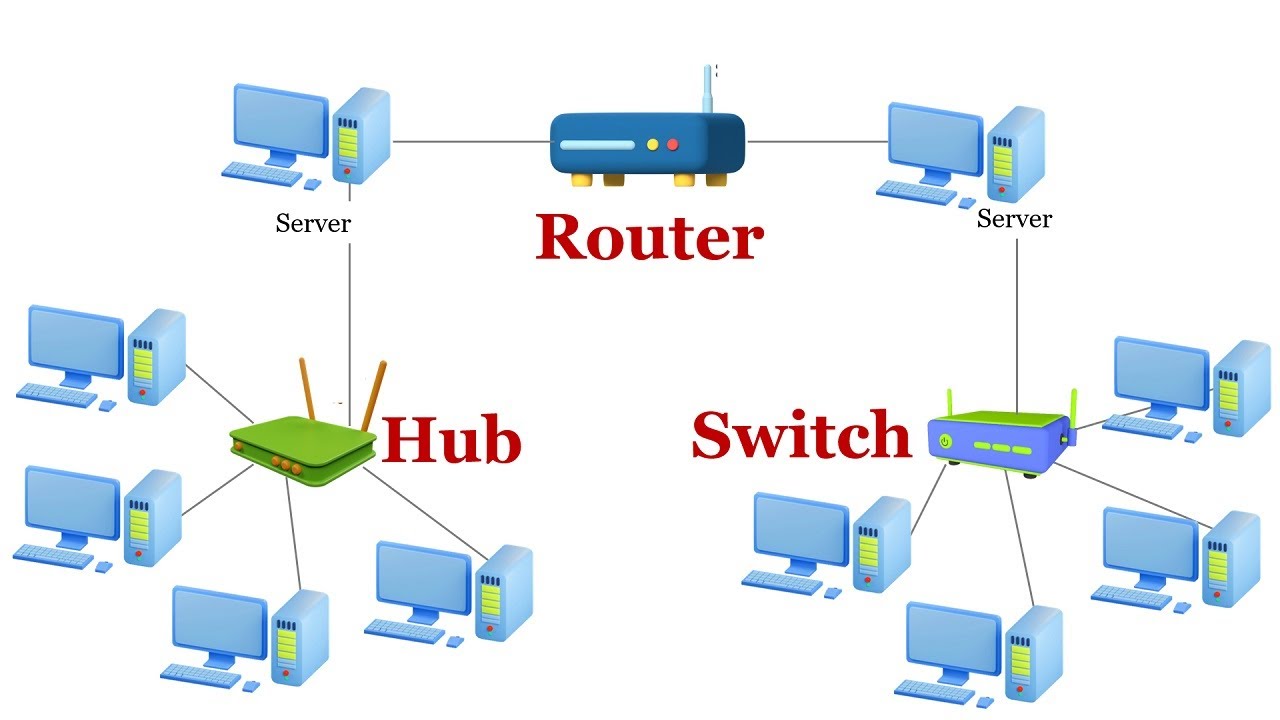
🔁 3. Switch
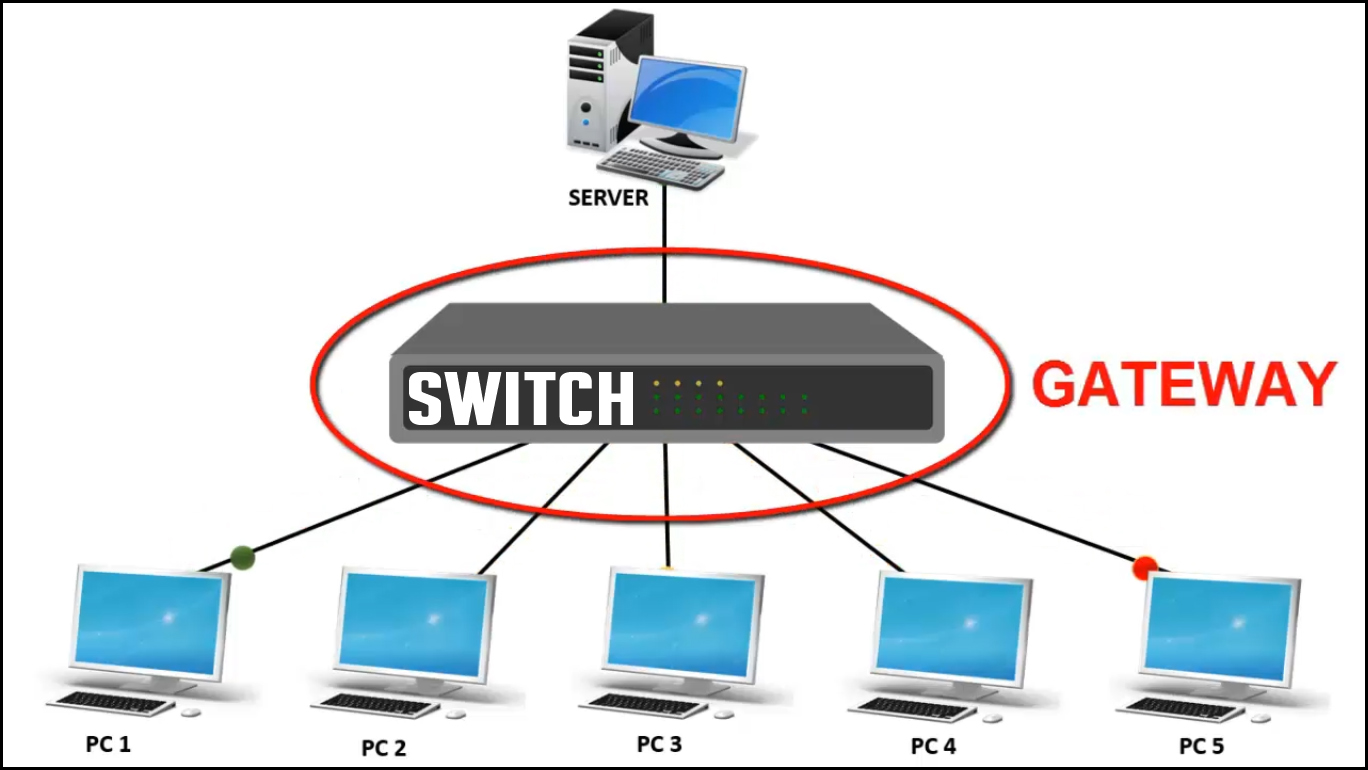
- Connects multiple devices within the same network (LAN)
- Uses MAC addresses to forward data only to the intended device
Used in LANs to efficiently direct traffic to correct devices.
🔌 4. Hub
Connects multiple devices in a network and sends incoming data to all connected ports.
- No intelligence – causes unnecessary traffic
- Slower and less secure than switches
Outdated, but was used in small networks to connect devices.
🌉 5. Bridge
Connects two separate LANs and filters traffic between them using MAC addresses.
Breaks up collision domains to reduce traffic and improve performance.
📡 6. Repeater
Regenerates and amplifies signals to extend the range of the network.
Used in wired or wireless networks when signal is too weak due to distance.

🌐 7. Gateway
- Connects two different networks using different protocols (e.g., TCP/IP ↔ Bluetooth)
- Translates data formats between two incompatible systems
Acts as a protocol converter between LAN and Internet, or between different systems.
🔥 8. Firewall
Monitors and controls incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined security rules.
Firewall Types Comparison:
| Feature | Stateless Firewall | Stateful Firewall |
|---|---|---|
| Memory | Doesn't remember past packets | Keeps track of connection state |
| Speed | Faster (less processing) | Slower (more processing) |
| Security | Basic security | More secure – knows connection context |
| Filtering | Based on IP, port, and protocol | Based on context and state |
| Use Case | Low-risk or high-speed environments | Enterprise networks, modern firewalls |
⚖️ 9. Load Balancer
Distributes network or application traffic across multiple servers to ensure no server is overwhelmed.
- Hardware Load Balancer: Physical device
- Software Load Balancer: Installed on a server or cloud (e.g., NGINX, HAProxy)
Improves availability, performance, and redundancy.
- Round Robin: Each server gets a turn
- Least Connections: New traffic sent to server with fewest connections
- IP Hash: Client IP determines the server
📊 Summary Table
| Device | OSI Layer | Purpose | Intelligence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Modem | Physical/Data Link | Converts analog/digital signals | Low |
| Router | Network | Routes packets between networks | High (IP-based) |
| Switch | Data Link | Connects devices in LAN | Medium (MAC-based) |
| Hub | Physical | Broadcasts data to all ports | None |
| Bridge | Data Link | Connects two LANs | MAC-based filtering |
| Repeater | Physical | Boosts signal | None |
| Gateway | All Layers | Protocol conversion | High |
| Firewall | Network | Packet filtering | Varies (Stateless/Stateful) |
| Load Balancer | Application/Transport | Traffic distribution | High (Algorithmic) |